Saccharomyces Boulardii Leading Authority in Naturopathic Endocrinology

The Gut Health Gurus Podcast – Podcast – Podtail
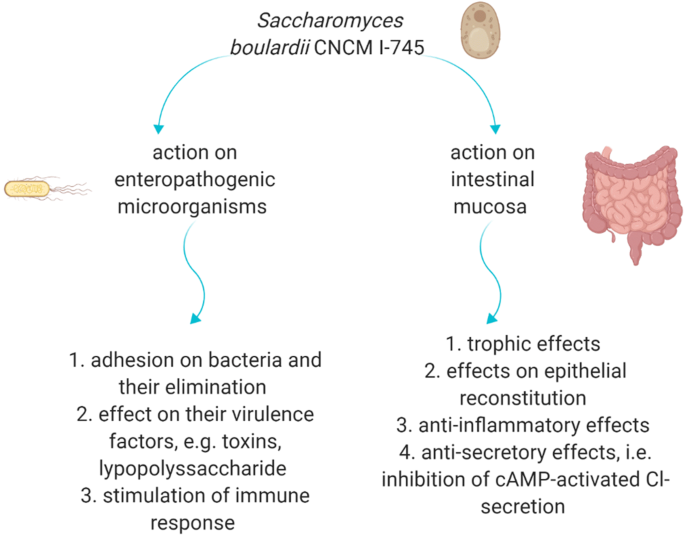
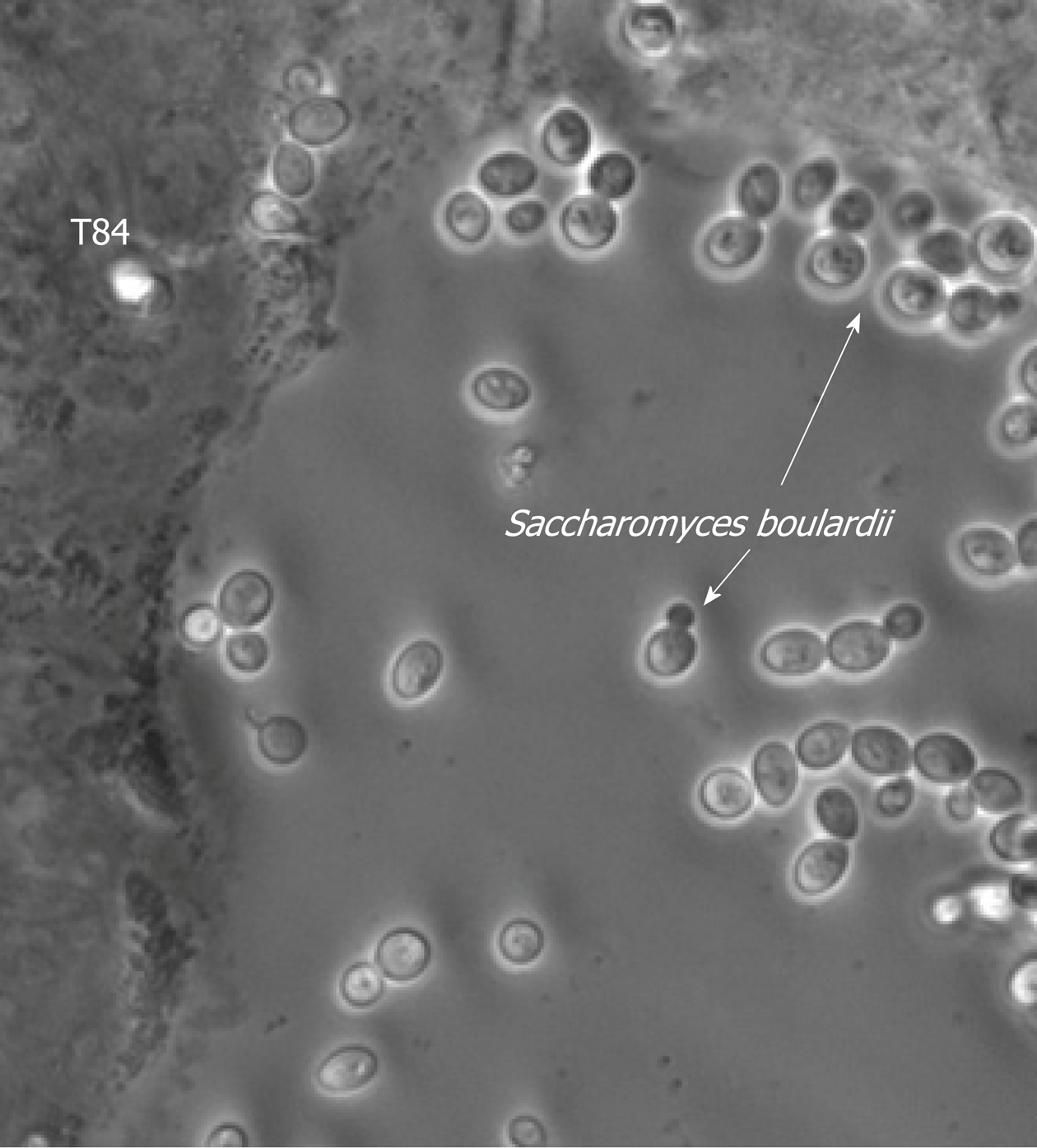
Saccharomyces boulardii CNCM I-745: A Non-bacterial Microorganism Used as Probiotic Agent in Supporting Treatment of Selected Diseases
Buy S. Boulardii Probiotic Capsules - Shelf-Stable 10 Billion CFU Saccharomyces Boulardii by Izabella Wentz Author of The Hashimoto's Protocol,

S. Boulardii Probiotic Capsules - Shelf-Stable 10 Billion CFU Saccharomyces Boulardii by Izabella Wentz Author of The Hashimoto's Protocol, Rootcology
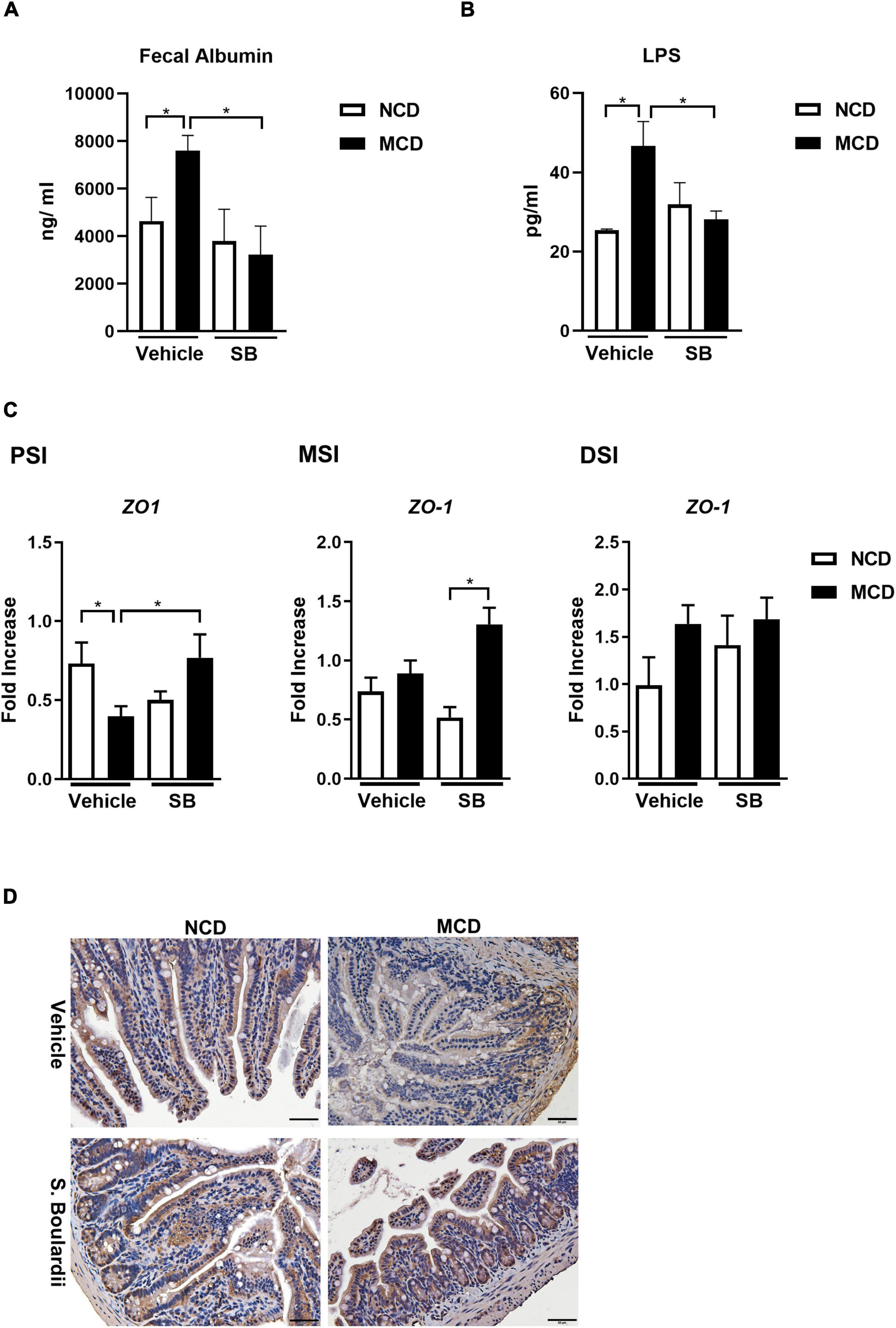
Frontiers Saccharomyces Boulardii Ameliorates Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis in Mice Induced by a Methionine-Choline-Deficient Diet Through Gut-Liver Axis
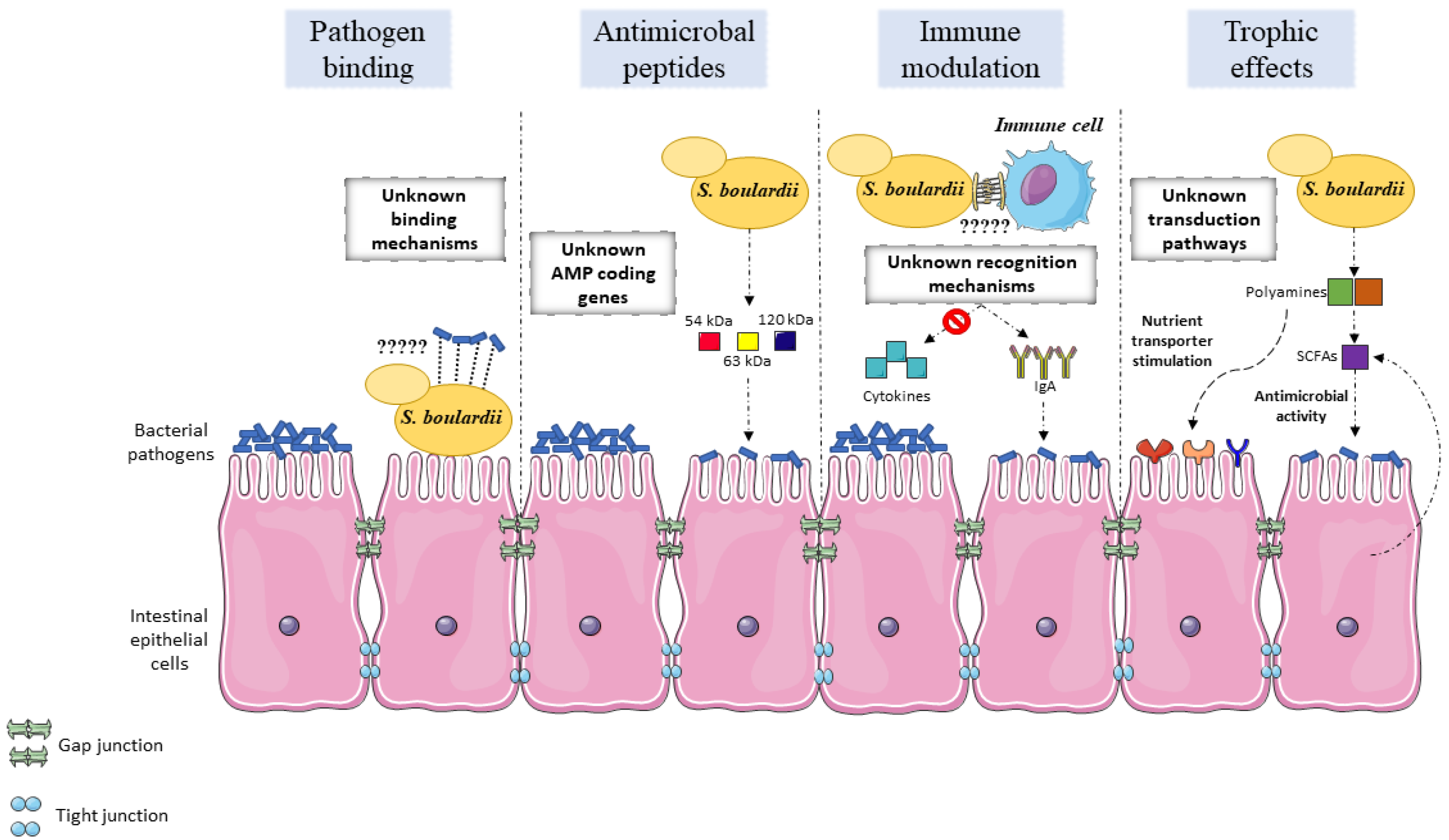
JoF, Free Full-Text
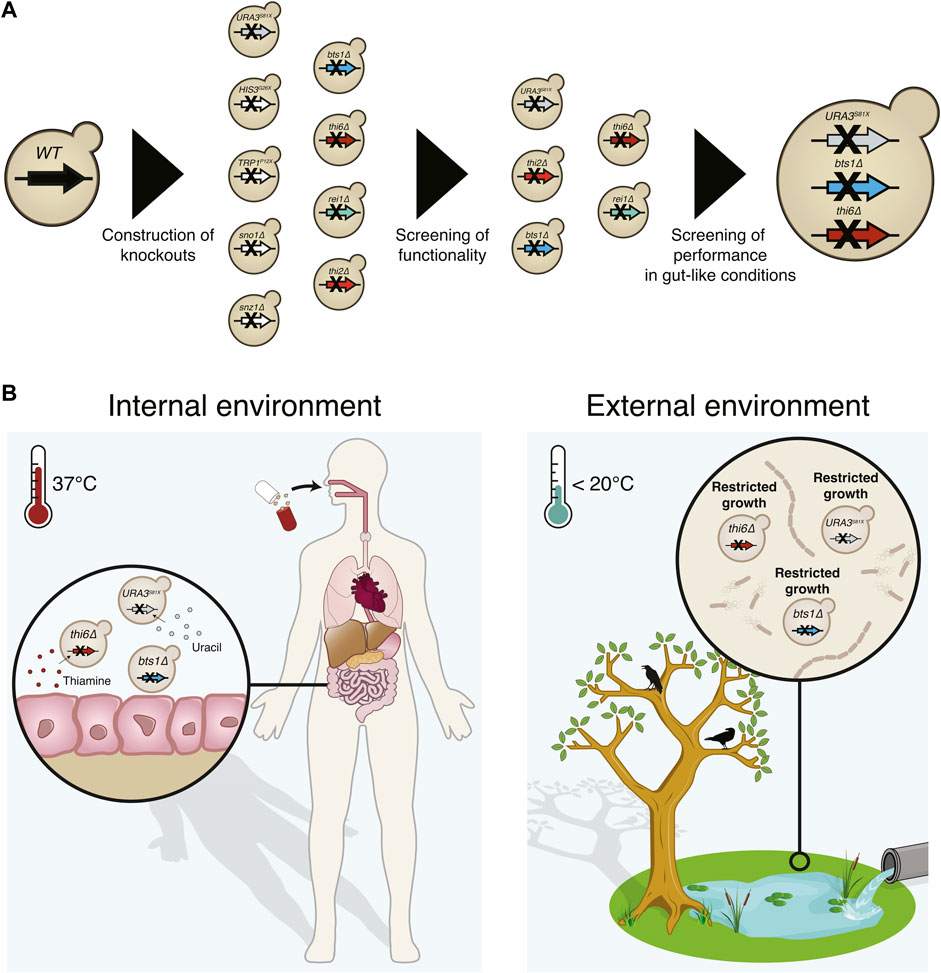
Frontiers Biocontainment strategies for in vivo applications of Saccharomyces boulardii

Holistic Therapist Magazine - Issue 37 by holistichealthmag - Issuu
A dietary supplement. Produces lactic acid and some B vitamins. It is a transitory microorganism.

Nutricology Saccharomyces Boulardii, Vegicaps, 50-Count
A probiotic, non-colonizing yeast species closely related to Brewer's yeast and not related to the yeast group to which Candida belongs. Saccharomyces boulardii taken orally supports the production of secretory IgA, and helps friendly probiotic bacteria to colonize the GI tract. * It is a transitory microorganism and is eliminated after supplementation is stopped. * Non-Dairy and Gluten-free.

Allergy Research Group Saccharomyces Boulardii
Is there any evidence that probiotic use alters the microbiome? - Quora
Should You Be Taking A Probiotic Every Day? Leading Authority in Naturopathic Endocrinology

Saccharomyces boulardii modulates oxidative stress and renin angiotensin system attenuating diabetes-induced liver injury in mice

Allergy Research Saccharomyces Boulardii, 60 Capsules - VictoriaHealth
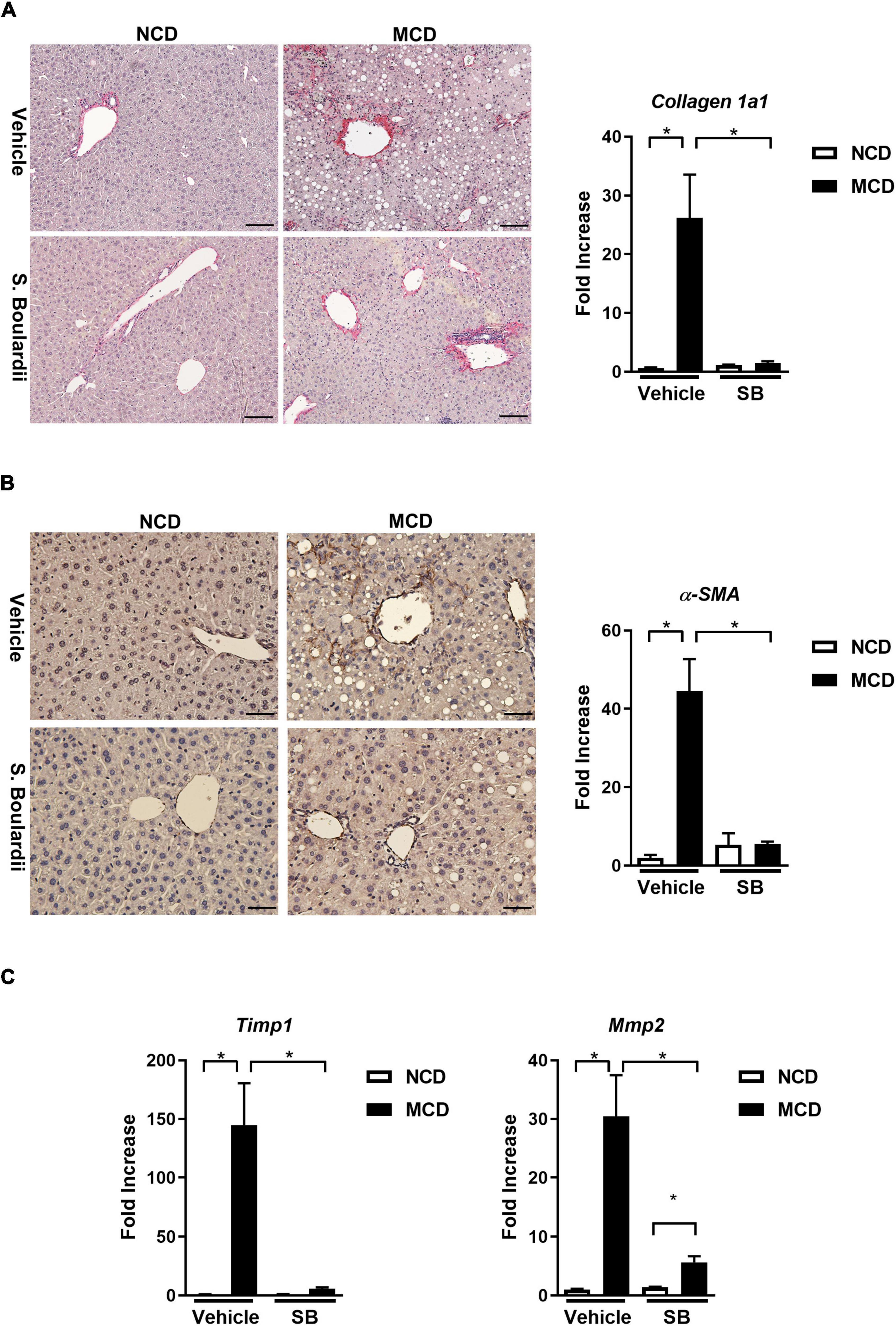
Frontiers Saccharomyces Boulardii Ameliorates Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis in Mice Induced by a Methionine-Choline-Deficient Diet Through Gut-Liver Axis

Organ Systems